2025 How to Choose the Right Well Casing for Your Drilling Project
In the realm of drilling projects, the significance of selecting the appropriate well casing cannot be overstated. Well casing serves as a fundamental component that ensures the integrity and safety of a well, protecting it from contamination and structural failures. According to Dr. Emily Peterson, a leading expert in well drilling and casing technology, "Choosing the right well casing is crucial for the success and longevity of your drilling project." Her insights underscore the impact that proper casing selection can have on operational efficiency and resource management.
As the industry evolves, understanding the various types of well casing materials, their properties, and their suitability for specific geological conditions becomes imperative. Factors such as depth, temperature, and pressure must be taken into consideration to ensure that the well casing can withstand the challenges present in different environments. Ultimately, the right decision in well casing can lead to enhanced performance, reduced maintenance costs, and greater environmental protection.
In this guide, we aim to explore the essential considerations when selecting well casing for your drilling project, providing you with the knowledge necessary to make informed choices that align with your operational goals. By understanding these critical aspects, you can navigate the complexities of well casing and contribute to the overall success of your project.
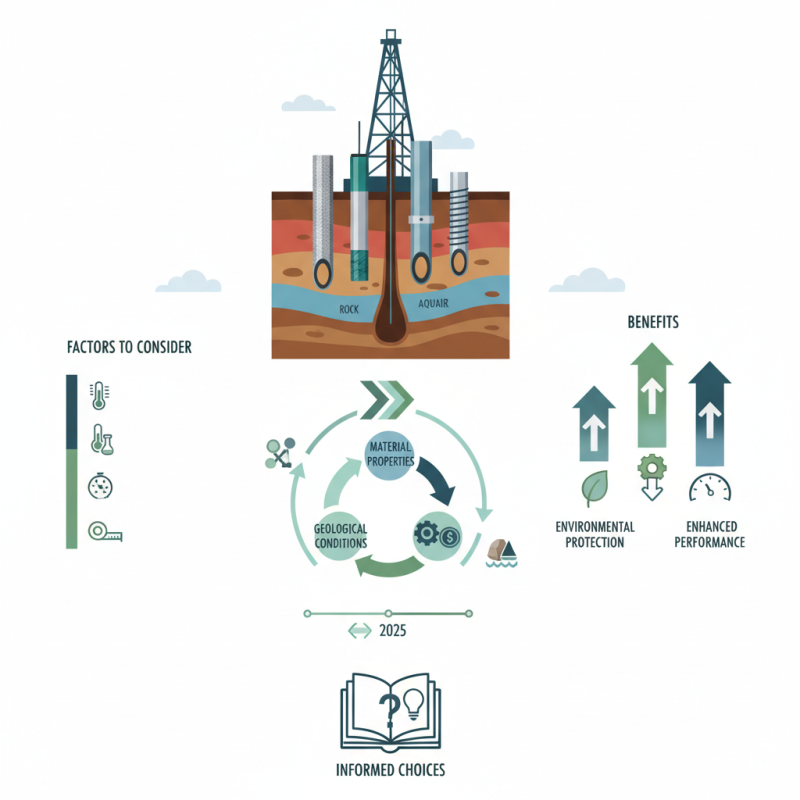
Understanding Well Casing: Its Importance in Drilling Projects
Well casing plays a crucial role in ensuring the integrity and sustainability of drilling projects. It acts as a protective barrier between the wellbore and the surrounding soil and groundwater, preventing contamination and maintaining the stability of the well structure. According to a report by the International Association of Drilling Contractors (IADC), improper casing can lead to significant risks, including groundwater contamination and well collapse, costing the industry millions in remediation efforts. This indicates the paramount importance of selecting the right casing material and design for the specific geological conditions encountered during drilling.
When choosing the appropriate well casing, several key factors must be considered, including the depth of the well, the characteristics of the geological formation, and the potential for corrosive materials in the environment. The American Society of Testing and Materials (ASTM) recommends regular assessment of these factors to mitigate risks effectively. For example, in areas prone to high water pressure or chemical exposure, opting for thicker, corrosion-resistant casing is crucial for the long-term success of the project.
Tips: Always conduct thorough geological assessments prior to drilling, as they provide critical insights into the types of casing needed. Collaborate with engineering experts who specialize in casing design to tailor solutions that fit specific project requirements. Regularly inspect and maintain existing casing to ensure that it continues to provide the necessary structural support and environmental protection throughout the life of the well.
Types of Well Casing Materials: Pros and Cons
When selecting the right well casing for your drilling project, understanding the different types of casing materials is crucial. Each material comes with its own set of advantages and disadvantages, affecting not only the integrity of the well but also its overall cost and maintenance. Common materials include steel, PVC, and fiberglass. Steel is known for its strength and durability, making it ideal for deep wells but prone to corrosion if not properly protected. On the other hand, PVC is lighter and resistant to chemicals, making it suitable for shallow wells but may not support heavy loads as effectively as steel.
When aiming for a long-lasting well, consider the environmental conditions of your drilling site. Areas with high acidity or salinity in the ground can significantly impact the choice of casing material. Tips to keep in mind include conducting thorough soil tests to assess corrosive potential and making sure to choose a casing that matches the specific requirements of the groundwater you are tapping into.
Additionally, while fiberglass casings are often resistant to corrosion and provide good insulating properties, they may not withstand high-pressure environments as effectively as steel. However, they can be a cost-effective alternative in certain scenarios. Evaluate the long-term viability of your well and plan for future maintenance and replacement costs when deciding on the casing material. Remember, the right choice will not only affect the well's performance but also your project's overall success.
Factors to Consider When Selecting Well Casing for Your Project

When selecting well casing for your drilling project, there are several critical factors to consider to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Firstly, understanding the geological conditions of the drilling site is essential. The type of soil and rock formations will influence the choice of casing material and thickness. For instance, in areas with unstable soil or high pressure, stronger and thicker casings may be necessary to prevent collapse and protect the integrity of the well.
Another significant factor is the diameter of the casing, which needs to match the specific requirements of the project. The casing diameter affects not only the flow rate of the water or oil but also the overall structural stability of the well. Additionally, compatibility with the drilling equipment and any potential future expansion plans should be carefully evaluated. This ensures that the casing installation will be efficient and adaptable to any changes in project scope or goals. Selecting the right casing is fundamental to the success and sustainability of the drilling operation.
Installation Techniques for Well Casing: Best Practices
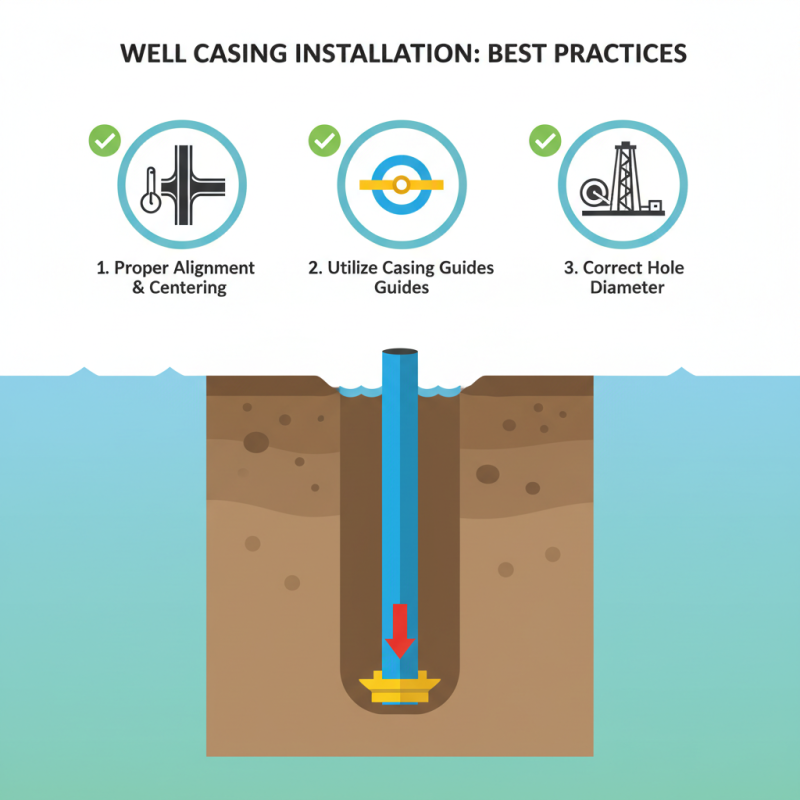
When it comes to well casing installation, employing best practices is crucial to ensure structural integrity and longevity of the well. One fundamental technique is the use of proper casing alignment during installation. This involves making certain that the casing is vertically straight and appropriately centered in the borehole. Utilizing a casing guide can be beneficial, as it helps maintain the correct orientation while reducing the risk of damage to the casing itself. Additionally, pre-drilling the hole to the correct diameter can minimize the chances of the casing becoming stuck during insertion.
Another essential aspect of well casing installation is the method of sealing the casing to prevent contamination and ensure stability. Cementing the casing is a widely practiced technique that involves pumping a cement slurry into the annular space between the casing and the borehole wall. It’s important to monitor the cementing process closely, ensuring that it completely fills the space and forms a good bond with both the casing and the surrounding formation. This practice not only prevents fluid migration but also enhances the overall strength of the well structure, providing a reliable vertical conduit for water or other resources. Proper monitoring of curing times and pressure can significantly impact the success of the installation process.
Regulatory Standards and Guidelines for Well Casing Selection
When selecting the appropriate well casing for a drilling project, it's imperative to adhere to regulatory standards and guidelines to ensure safety, sustainability, and efficiency. The American Petroleum Institute (API) sets forth strict standards for well casing materials and installation, focusing on the integrity and performance of underground aquifers. According to the API's recent data reports, nearly 40% of well failures can be traced back to inadequate casing practices, underscoring the importance of compliance with regional regulations to mitigate environmental risks.
Moreover, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) provides comprehensive guidelines that emphasize the need for the selection of materials that can withstand local geological conditions. For instance, regions with high corrosive potential may require non-corrosive materials or special coatings to preserve casing integrity over time. A report by the National Ground Water Association (NGWA) suggests that using the appropriate casing not only prolongs the lifespan of the well but also enhances groundwater protection, reducing contamination risks by up to 50%. Casing diameter, wall thickness, and sealant type are also critical factors to consider, as they must align with both state regulations and the specific hydrological context of the drilling site.
Ensuring compliance with these guidelines not only safeguards water resources but also fosters public trust. A study by the Ground Water Research Group has shown that projects adhering to regulatory standards report fewer incidences of contamination and operational disruptions. Hence, thorough attention to regulatory advice not only meets legal obligations but also emphasizes a commitment to responsible resource management.
2025 How to Choose the Right Well Casing for Your Drilling Project - Regulatory Standards and Guidelines for Well Casing Selection
| Casing Diameter (inches) | Material | Regulatory Standard | Maximum Depth (feet) | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | Steel | API Spec 5CT | 2000 | Geothermal Wells |
| 6 | Fiberglass | ASTM D2996 | 1500 | Water Wells |
| 8 | Steel | API Spec 5CT | 5000 | Oil and Gas Wells |
| 10 | PVC | ASTM F480 | 800 | Monitoring Wells |
| 12 | Composite | ISO 9001 | 3000 | Industrial Drilling |
Related Posts
-

Essential Guide to Choosing the Right Water Well Supplies for Sustainable Water Management
-

2025 How to Find the Best PVC Supplies for Your Projects
-

2025 Top 10 Well Supplies to Enhance Water Quality and Efficiency in Your Home
-

Top 5 Pipe Supplies You Need for Successful Plumbing Projects in 2023
-

4 Tips for Choosing the Right Steel Pipe for Your Project Requirements
-

Understanding the Benefits and Applications of PVC Water Pipes in Modern Plumbing Systems
